Hospitals and Six Sigma
Dr. Jonathan Phillips
A previous blog post referenced the To Err is Human report that was published in 2000. This report was the inciting force behind improving healthcare quality in the United States. As payers and regulators become the stakeholders in the cost and outcomes of healthcare, healthcare systems must now approach quality improvement (QI) through many different experiences. These approaches may focus on reducing waste, making workflows more accommodating to employees, workplace standards of organization, or reducing the variability and results of practice and procedures.
One approach that has been used extensively in the manufacturing industry is Six Sigma, which focuses on a standardized statistical approach to control processes with support from upper management and down.
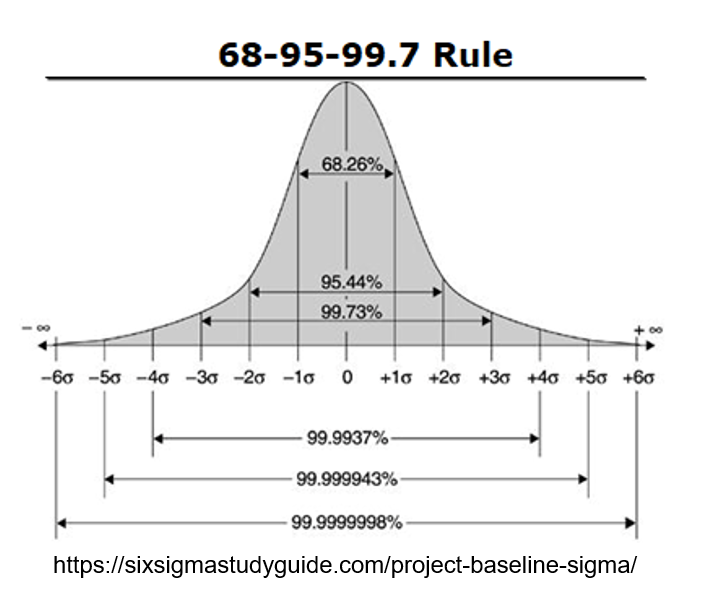
Sigma is the unit of measurement for standard deviation. Standard deviation is the amount of variability within a data set from the mean. Two standard deviations from the mean includes 95% of the data set. This is what is typically used in research to convey statistical significance.
Six Sigma gets its name from the idea that their goal is to have a failure rate of six deviations from the mean. This would be a failure rate of 3.4 per million and is the goal set by businesses/individuals that choose Six Sigma.
Individuals who choose to train in Six Sigma will often follow a defined and graduated approach to training: First, participants in entry-level roles will often begin with a Yellow Belt. Individuals who have gained experience and are able to operate with senior Six Sigma officials will obtain a Green Belt. Finally, individuals who can lead teams and effectively apply Six Sigma principles to problems through a standardized approach will earn a Black Belt.
Six Sigma follows a standardized approach referred to as the DMAIC process.
Define: Stakeholders and team leaders identify problems and a large-picture approach to solving the identified problem including through the use of process maps
Measure: Gather and interpret data through maps, analysis, and charts to accrue information to make future decisions
Analyze: Analyzing processes for underlying errors or inadequacies within a system. This may use Fishbone Diagrams, Process Maps, or various Root Cause Analyses.
Improve: Focused plans that are designed to address underlying systemic processes that have errors. They may also focus on efficiency and waste reduction through processes such as Kaizen events
Control: Making the change sustainable. Equipping stakeholders, from front line workers to upper management, with tools that will provide sustained success.
Six Sigma has been utilized most often in North American healthcare, particularly in the United States. A recent systematic review of publications recently categorized the end results of Six Sigma into 3 categories:
Reduction of time
Reduction of errors
Reduction of costs
All of these categories have tangible benefits to both the patient and the larger healthcare system.
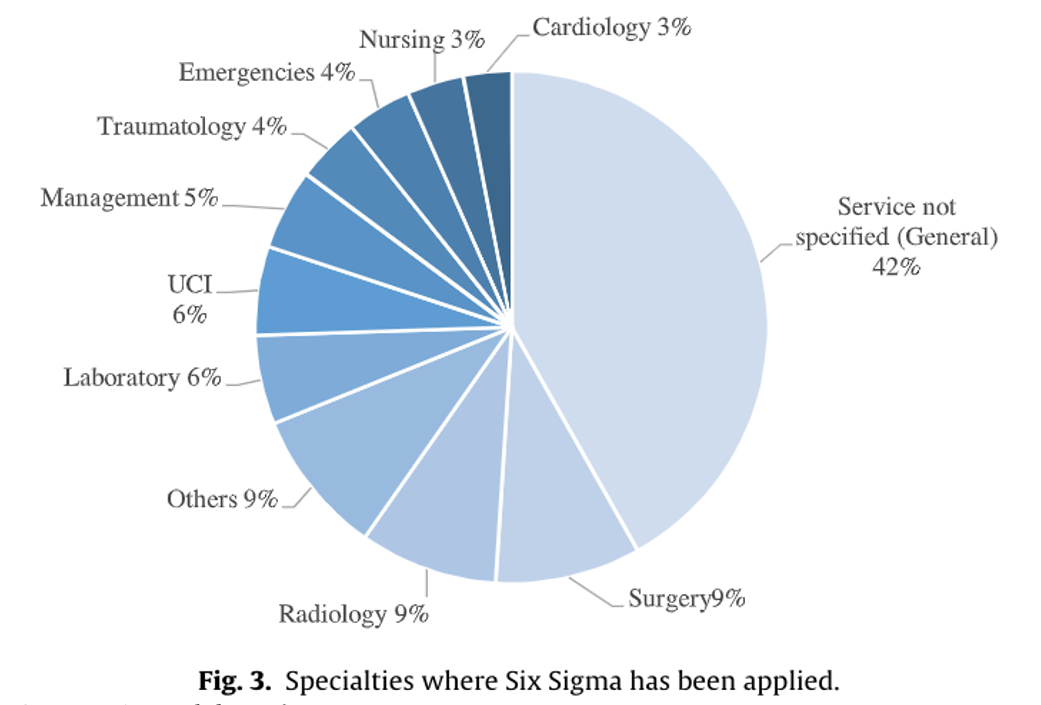
While manufacturing has long known of the cost savings and improvements in both products and worker experience, healthcare is still catching up on identifying the benefits that QI processes such as Six Sigma may bring. One systematic review was able to identify and review 382 published articles pertaining to Six Sigma QI. Interestingly, these were initially almost exclusively published by professional practitioners. Over the past ten years, academic publications and joint academic/professional publications have increased significantly to contribute to the literature. A majority of these publications are case studies, and when listed--surgical and radiology specialties have published more publications than other specialties. A wide variety of improvements have been disseminated, including decreased infection rates, decreased length of hospital stay, decreased fall rates, and decreased medication errors. Patients benefit from improved care, and healthcare practitioners benefit from working in an environment with less opportunities for harm.
Healthcare organizations will adopt successful processes as they are duplicated across multiple sites and organizations. Six Sigma is only one of the tools used by practitioners in Quality Improvement. Future blog posts will continue to discuss other methodologies with a focus on efficiency and healthcare provider experiences.
Are you interested in obtaining Six Sigma certification? Organizations such as the American Society for Quality (ASQ), and several others, offer e-learning training for yellow belt projects to assist with jump-starting Six Sigma projects. Have you considered earning Six Sigma certification? If so, let us know in the comment section below!
Jonathan Phillips, D.O.
University of Louisville | Internal Medicine and Pediatrics
Dr. Jonathan Phillips is PGY-4 resident at the University of Louisville for Internal Medicine and Pediatrics. He attended Kentucky Wesleyan College for his undergrad and completed medical school at the Kanas City University of Medicine and Biosciences.
References
What is Six Sigma? American Society for Quality. Accessed September 6,2021. https://asq.org/quality-resources/six-sigma
The Define, Measure,, Analyze, Improve, Control (DMAIC) Process. American Society for Quality. Accessed September 6, 2021.https://asq.org/quality-resources/dmaic
What is Six Sigma? American Society for Quality. Accessed September 6,2021.https://asq.org/quality-resources/six-sigma#Certifications
Niñerola A, Sánchez-Rebull M-V, Hernández-Lara A-B. Quality improvement in healthcare: Six Sigma systematic review. Health policy. 2020;124(4):438-445. doi:10.1016/j.healthpol.2020.01.002
Hessing, Ted. How To Determine Baseline Project Sigma. Accessed Septemver 6, 2021. https://sixsigmastudyguide.com/project-baseline-sigma/